INTRODUCTION
The seamless operation of base station antennas is of utmost importance for efficient and reliable communication networks. However, these antennas are constantly exposed to various environmental factors that can affect their performance and structural stability. Among these factors, wind load plays a significant role. Wind load is a crucial parameter when it comes to designing the structure of base station antennas, including the tower and supporting structures. It can cause structural damage, misalignment, and signal degradation. Therefore, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of wind load and effectively manage it in order to ensure optimal functionality of base station antennas. With the rapid advancement of MIMO technology in recent years, antennas are becoming more integrated and their size is continuously increasing. This has raised concerns about the impact of wind load on the tower and the overall antenna system. Accurately estimating wind load is vital as it helps determine the appropriate materials, dimensions, and mounting methods for base station antennas. This ensures the structural integrity, stability, and ultimately the performance and reliability of the antennas. Additionally, it contributes to the overall safety and economic efficiency of the communication network.
OUR ESTEEMDED CLIENT
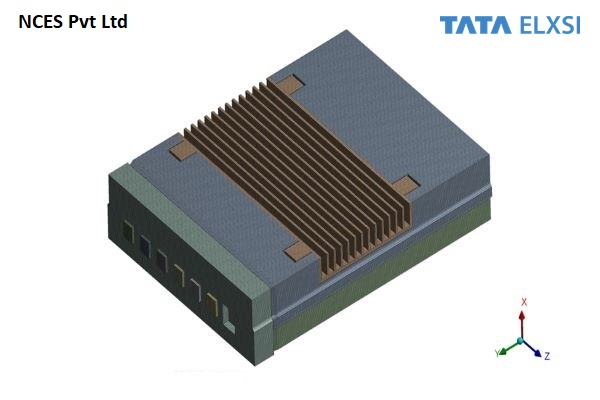
Our esteemed client is a subsidiary of the renowned Tata Group, which happens to be India's largest conglomerate. They are currently engaged in the development of a cutting-edge 5G Remote Radio Unit (RU) that complies with the ORAN 7.2x standards. Recognizing our expertise in the field, the client has entrusted us with the responsibility of conducting Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis for the Remote Radio Unit to assess the thermal performance of the existing design of the Remote Radio Unit and to recommend design changes for enhancing the heat transfer. We are honored to have been chosen for this significant project and are committed to delivering exceptional results.
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS FOR WIND LOAD CALCULATION
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis enables engineers to simulate and analyze airflow patterns and pressure distribution around baseband antennas. By utilizing CFD, designers can accurately assess the wind load effects on antennas, identifying areas of high stress, turbulence, and potential vibration. This information allows for informed design modifications and optimization to enhance the antenna's performance and structural resilience.
PROJECT OVERVIEW
Our esteemed client is a subsidiary of the renowned Tata Group, which happens to be India's largest conglomerate. They are currently engaged in the development of a cutting-edge 5G Remote Radio Unit (RU) that complies with the ORAN 7.2x standards. Recognizing our expertise in the field, the client has entrusted us with the responsibility of conducting Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) to simulate and analyze airflow patterns and pressure distribution around the antenna and remote radio unit. We are honored to have been chosen for this significant project and are committed to delivering exceptional results.
DESCRIPTION OF CAD MODEL CONSIDERED FOR CFD ANALYSIS
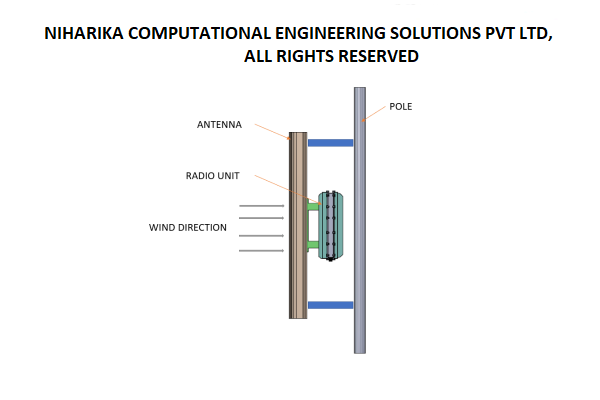
The wind load aerodynamics analysis is conducted on the CAD model, which includes an antenna, remote radio unit, mounting bracket, and pole.
CFD MESH
The Poly-Hex core elements are used to mesh the simplified CAD model. The mesh size amounts to 32 million, and it is refined in the boundary layer region to meet the y plus requirement.
FLOW MODELLING
The flow is modeled as 3D, steady state, incompressible, viscous, and turbulent. The turbulence closure is represented by the K-Omega SST Turbulence model (with a y plus value of 0.8).
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
CFD analysis is conducted for wind velocities ranging from 150 to 200 kilometers per hour.
The CFD analysis outcomes have allowed us to observe and examine the flow pattern, pressure distribution, turbulence, and vortex zones. Through simulating various wind directions and analyzing the findings, we have obtained the conservative pressure distribution for all the systems that were taken into account during the CFD analysis.

We Got More
Go through All Our Case Studies
CFD analysis of Multi Band Remote Radio Unit
The advent of 5G technology has brought about unprecedented advancements in wireless communications, enabling faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. These advancements are associated with higher power consumption and increased heat generation in the 5G Remote Radio units.Increasing data rates and network densification require radio units to process larger volumes of data, leading to higher power consumption and heat generation. Environmental factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and exposure to direct sunlight also impact the thermal aspects of the radio units. Read MoreDEVELOPMENT OF COOLING SOLUTION FOR GaN RF POWER AMPLIFIER
The demand for high-power and efficient radio frequency (RF) power amplifiers has been steadily increasing across various industries, including wireless communications, radar systems, and satellite communication. GaN (Gallium Nitride) technology has emerged as a game-changer in RF power amplification due to its exceptional performance characteristics and advantages over traditional technologies. GaN technology offers higher power density, improved efficiency, and wide bandwidth capability, setting it apart from traditional technologies like GaAs (Gallium Arsenide) or SiC (Silicon Carbide). Read More
AERODYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF TELECOM TOWER STRUCTURE
By meticulously considering the principles of aerodynamics in the design of telecom towers, engineers can effectively reduce wind induced vibrations. This not only enhances the overall experience for everyone but also guarantees the towers long term structural integrity and stability. Read More
Structural analysis for Triband Radio unit with antenna
In this project, we performed FEM analysis to check strength of the triband antenna model for the given load conditions. FE mesh consists of higher-order Tet elements & Hexahedral elements. Mesh size is 2810173 nodes & 1611495 elements. Appropriate contacts are modeled between all the parts in the assembly. FEM analysis is carried out as per the load conditions provided by the customer. We carried out Modal Analysis, Sine sweep Analysis (Harmonic Analysis), Random Vibration Analysis, Shock Analysis, Seismic Analysis, and Wind load Analysis. Read More
Structural analysis for 5G Remote Radio Unit
The advent of 5G technology has revolutionized the telecommunications industry, ushering in a new era of ultra-fast data speeds, low latency, and advanced network capabilities. Amidst this transformative landscape, the 5G Remote Radio Unit (RRU) emerges as a critical component, playing an instrumental role in the deployment and optimization of 5G networks. With 5G networks, RRUs have evolved to handle higher data volumes and faster speeds. They are designed to support an increasing number of devices and provide seamless connectivity even in densely populated areas. These modern marvels are a testament to the incredible progress made in wireless technology. Read More