JSW-ALMATTI PUMPING STATION : OVERVIEW
For meeting the operational water requirements of the 12 MTPA integrated steel plant complex at Vijayanagar works, JSW Limited has commissioned a raw water pumping system with a capacity of 40 MGD installed at Almatti (Narayanapua Dam-Krishna River), which is 170 Km away from the plant location. The pumping scheme consists of an Intake pump house at 0 KM chainage at Marol, an Intermediate Pumping Station at 28.5 Km Chainage at Ilkal, a break Pressure Tank at 90 Km Chainage at Methagal, and a total length pipeline of 170 Km consisting of 90 Km Pressure Main & 80 Km Gravity Main. To cater to additional water requirements for plant expansion at the 18 MTPA stage, augmentation of the existing pumping system to 50 MGD is proposed and the project is in the final stage. The Intermediate Pumping Station at Ilkal consists of three vertical turbine pumps (two working and one standby). The specification of each pump is: 4750 m3/hr volume flow rate, 145-meter delivery head, and 2400 KW Motor rating. Recently, for the past two years, the JSW team has been experiencing abnormal resonant vibrations in the existing pumping system at the Intermediate Pumping Station in Ilkal, after almost trouble-free operation for 10 years. In light of the above, JSW Limited awarded a turnkey contract to Niharika Computational Engineering Solutions Pvt Ltd (NCES) to carry out diagnostic studies, investigate the root cause and provide necessary feasible corrective measures to eliminate the resonant vibration in the pumping system at the Intermediate Pumping Station in Ilkal.

RESONANT VIBRATIONS IN THE VERTICAL TURBINE PUMPS
Vertical Turbine Pumps manufactured and commissioned by Kirloskar Brothers Limited in 2010 have a specification of 4750 m3/hr volume flow rate and 145-meter delivery head. 2400 KW HT Motor is supplied by Bharath Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL). According to the specifications mandated by Kirloskar Brothers Limited, the natural frequency of the supporting structure for the pump and motor should be at least 25% above the pump operating speed of 745 RPM at full load (synchronous speed 750 RPM). However, it must not be less than the guidance given in API 610 clause 8.3.5 relating to dynamic analysis. As per the clause, "Generally, a 20% margin of separation should be maintained between the natural frequency of the motor support structure and the operating speed." To identify the root cause of the resonant vibrations, the NCES team has conducted detailed vibration measurement & analysis and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for mechanical structures. Detailed investigations are carried out to identify any faults and integrity issues in the reinforced concrete structural members that may contribute to the higher vibration levels of the VT pump unit. Non-destructive and semi-destructive tests are conducted for all the reinforced concrete structures to assess their soundness and present condition by a competent laboratory accredited by NABL. Our strong domain knowledge, leveraged with all the above investigation results, has resulted in a comprehensive engineered solution that efficiently addressed the vibration issues faced by the JSW team and ensured smooth, trouble-free operation of the VT pumps.

JSW Limited awarded a turnkey contract to Niharika Computational Engineering Solutions Pvt Ltd (NCES) to carry out diagnostic studies to fix the root cause and provide necessary feasible corrective measures to eliminate resonant vibration in the pumping system at the Intermediate Pumping Station, Ilkal. The scope of the work also includes extending all investigations to the other two pumping stations: the Intake Pumping Station at 0 KM chainage at Marol and the upcoming Pumping Station adjacent to the 28.5 Km Chainage at Ilkal (which is currently under construction), in order to prevent any similar vibration issues in the future. As part of the overall process, the NCES team has conducted non-destructive and semi-destructive testing to assess the integrity and current condition of the reinforced concrete structural members, vibration measurement and analysis, and Finite Element Analysis for mechanical and structural members for all three pumping stations owned and operated by JSW Limited.
VIBRATION MEASUREMENT AND ANALYSIS
NCES team has conducted a detailed vibration measurement and analysis of all three pumps operating in the Ilkal pumping station. For the purpose of the vibration study, measurements were taken on each pump and also on the floor adjacent to the motor supports. Measurements were taken for the solo operation of each pump, different operating combinations of the pumps and worst-case scenario of all the three pumps in parallel operation. In addition to the above, a bump test of each motor and motor floor, as well as a coast down measurement on the motor in a decoupled condition, were carried out. Operating Deflection Shape (ODS) analysis of individual pumps in solo operating condition is carried out. It was found that among the three pumps in the Ilkal pumping station, one of the motor driving pumps is operating very close to its resonance frequency, and the vibration level of this pump exceeds the limit level of 4.5 mm/s (as per ISO 10816-3 standard). The operating speed of this particular motor is 745 rpm (12.5 Hz), whereas its resonance speed, as determined by vibration analysis, is 735 rpm (12.25 Hz). This is the main reason for the higher vibrations in the motor of this pump. These vibration measurement results are used to validate the Finite Element Analysis (FEA) model to gain confidence in the further optimization strategy employed to resolve the resonant vibration issues. Decades of experience in conducting dynamic FEM analysis, strong fundamentals in the vibration subject have enabled the NCES team to deliver the right solution to JSW Limited to address the resonant vibration issues and ensure smooth, trouble-free operation of the pumps.

FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS : MECHANICAL SYSTEMS
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is carried out to establish the current natural frequency of the supporting structure of the pumping system, which includes the pump, motor, piping connection, and all supporting structures. The NCES team developed a 3D CAD model of the complete pumping system, including the stator and rotor, stator and neutral terminal boxes, thrust bearing housing, motor stool, sole plate, pump base, discharge tee, thrust rods, column pipes, pump bowls, impellers, bell mouth, shafts, muff couplings, bearings, and strainer mesh. The dimensions of these components were obtained from the cross-sectional assembly drawing provided by the JSW team. FE model was developed using modelling software package Altair Hypermesh, and the analysis was carried out using LS-DYNA, a general-purpose finite element software. The model was primarily developed using solid elements, with plate elements being used where necessary. Bolted connections between different components were modelled as rigid connections with no failure, except for the connection between the motor stool and the sole-plate. Since the design of the pump and motor was proprietary, the detailed dimensions and construction of the pump-motor assembly were not available, and several assumptions were made while developing the finite element model. To have confidence in the validity of the results, the model was validated using physical vibration measurement results, as explained in the previous section.

FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS : CIVIL STRUCTURES
A part of this diagnostic study is to develop a 3D model of the civil structural members and compute the natural frequencies of the civil structures in order to verify their influence with the resonant vibration of the pumping system. A 3D CAD model of the civil structural members is developed using PTC Creo software based on the 2D drawings provided by the JSW team, and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is carried out using commercial FEA software. Modal analysis results indicate that the natural frequencies of the civil structural members are sufficiently far away from the pump operating frequency (12.5 Hz). The natural frequency of civil structures varies between 2 to 3 Hz, and such frequencies fall beyond a 75% difference from the pump operating frequency, against the minimum specified 25% difference.

CONDITION ASSESSMENT OF CIVIL STRUCTURAL MEMBERS
A detailed condition assessment study was conducted for the civil structures at the Intermediate Pumping Station in Ilkal to investigate their present condition. Non-destructive condition assessment tests, such as rebound hammer test, ultrasonic pulse velocity test, carbonation test, and electrochemical half-cell potential meter test, were carried out in accordance with industry standards at an NABL accredited laboratory. The condition assessment study concluded that the existing civil structures at the Intermediate Pumping Station in Ilkal are in good condition, with no significant distress observed. The vibration levels experienced in the RCC floor adjacent to the pumps are not due to structural defects or deterioration in the reinforced concrete members. Restoration measures are recommended for the distressed reinforced concrete members to restore them to their normal condition and prevent further deterioration.

PROPOSED SOLUTION
Scientific decisions are made based on the analysis of measured vibration data, Operating Deflection Shape (ODS) analysis, and Finite Element Analysis for various operating load conditions in order to enhance the stiffness of the motor supporting stool. New stiffeners are designed to improve the stiffness of the pumping system, ensuring that the natural frequencies are at least 25% different from the operating frequency. The revised design is validated using Finite Element Analysis.

PERFORMANCE POST IMPLEMENATION
After the implementation of the solution engineered by the NCES team, all the pumps have been operating without any vibration issues for six months. This is similar to the condition ten years ago when Larsen and Toubro Limited handed over the pumping station to JSW Limited.
We Got More
Go through All Our Case Studies

Pollution dispersion studies for SABIC chemical plant stack using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
We executed this project for a SABIC chemical plant in Al Jubail, Saudi Arabia. The objective of the project is to dilute the concentration of pollutants in the high-rise stack by injecting steam generated from the waste heater boiler. We carried out CFD analysis and analyzed the reduction in the concentration of pollutants. We designed a sparger which enabled us to increase the effective height of the stack. Read More
Cement grinding plant Roller shaft re-design and FEM analysis
Frequent failure of the shaft used in cement grinding units at our customers plants across India warranted an independent review of the shaft design. Niharika Computational Engineering Solutions Pvt. Ltd. (NCES) was chosen for this Independent review task using the finite element method. NCES was provided with information on the working principles of the roll press system and also information on the material used for the shaft that is in question, along with detailed drawings. To better understand the design of the shaft for various loads that it would see during normal operation, a comprehensive study was undertaken by the NCES team. This study involved using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and performing static analysis for load distribution, modal analysis for estimating natural frequencies, rotor dynamics for checking resonance due to vibration, and dynamic analysis to estimate endurance limit under complex loading and crack initiation and propagation. NCES team has modified the shaft design and recommended a new material that addresses the frequent failure of the shaft. Read More
Structural analysis of crude oil storage tank
The scope of the work is to validate the structural design of a 32 Kilo Litre crude oil storage tank employed in the Adani Petrochemical plant. Our customer has approached us to validate the tank and cone roof design using Finite Element Analysis (FEA). We conducted FEM analysis, worked collaboratively with our customer, and enabled them to address all the minor uncertainties. In the end, we concluded that the design met all the structural requirements. Read More
CFD analysis of Wind turbine Generator unit
This project is executed for Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy. The objective is to conduct CFD analysis for the Wind Turbine generator (WTG) unit at the assembly level and to estimate the temperature developed on all the subsystems We carried out CFD analysis for two configurations, a) The existing configuration consists of four exhaust fans on top of the WTG system and converter refrigerant cooling fan capacity is 1.5 KW. b) The proposed configuration with three exhaust fans at the top of the WTG system and converter refrigerant cooling fan capacity is enhanced to 2.6 KW All the major subsystems in the WTG unit, like transformers, Generator & slip ring system, converter panel, gearbox unit, hydraulic oil tank and converter coolant (refrigerant) systems are considered in the CFD analysis. Read More
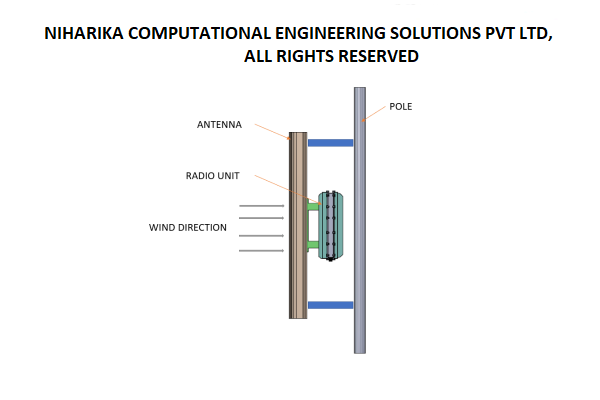
CFD analysis of Multi Band Remote Radio Unit
The advent of 5G technology has brought about unprecedented advancements in wireless communications, enabling faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. These advancements are associated with higher power consumption and increased heat generation in the 5G Remote Radio units.Increasing data rates and network densification require radio units to process larger volumes of data, leading to higher power consumption and heat generation. Environmental factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and exposure to direct sunlight also impact the thermal aspects of the radio units. Read More