ANAEROBIC DIGESTER CFD analysis : TO ENSURE OPTIMAL MIXING
Anaerobic digestion refers to the breakdown of biodegradable materials facilitated by various bacteria and archaea in an oxygen-free environment. The resulting biogas primarily consists of methane (50–60%) and carbon dioxide (30–40%), generated through the anaerobic digestion process. Several critical factors influence the efficiency of anaerobic digestion, including the characteristics of the substrate, feeding strategies, hydraulic retention time, pH levels, temperature, and mixing dynamics. Among these factors, mixing is particularly vital for enhancing the anaerobic digestion process and maximizing biogas production. Effective mixing within the digester promotes biological, chemical, and physical uniformity, preventing the creation of dead zones that hinder substrate conversion. Insufficient mixing can lead to reduced digester performance, while excessive mixing may disrupt the digestion process due to high shear forces. Therefore, it is essential to thoroughly understand and examine the optimal mixing techniques in anaerobic digesters.

OBJECTIVE OF CFD ANALYSIS
A gas nozzle system has been developed by our customer, which injects biogas from the base of the digester following a specific operational sequence. The nozzles, arranged circumferentially, will function in a sequential manner, ensuring that the sludge remains in a uniform state. A 3D transient viscous turbulent multiphase CFD analysis has been conducted for the bio digester tank. The operational sequence of 20 gas nozzles is implemented through a user-defined function (UDF). Eulerian multiphase modeling is utilized to simulate the transport of sludge constituents. The mixing process is meticulously examined during the operational sequence to assess the effectiveness of the gas nozzle sequence.
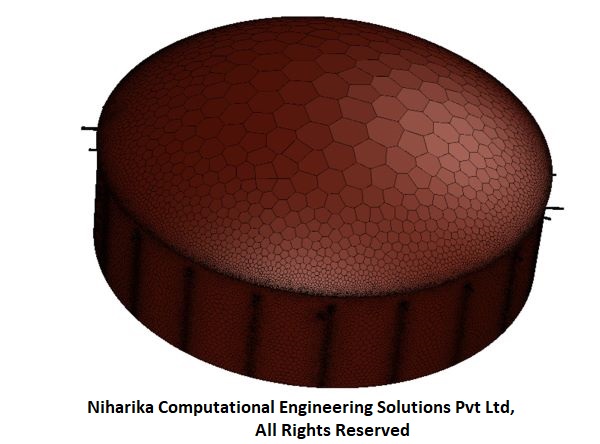
CFD MESH
The CFD mesh is composed of poly-hex core elements, ensuring adequate boundary layer resolution within the gas nozzle ducting system. The total mesh count is 18 million, achieving optimal quality metrics in accordance with established CFD practices.
CFD SOLVER SETUP
The flow within the anaerobic digester is represented as a three-dimensional, time-dependent, viscous turbulent multiphase system. The turbulence is characterized using the K-Omega turbulence model. To simulate the transport of sludge components, an Eulerian multiphase modeling approach is utilized. The operational sequence for 20 gas nozzles is executed via a user-defined function (UDF).
CFD analysis results : Homogeneity in the sludge
The sludge is a mixture of Napier grass and press mud as the main constituents in a water medium. Napier particles constitute about 15 % of the sludge, with an average particle size of 2 mm. Biogas stored in the top dome portion of the digester is recirculated through a compressor connected to the nozzle unit, in a pre-determined Nozzle operating sequence to achieve agitation. A consistent volume fraction of Napier grass particles indicates that the mixing process is optimal.
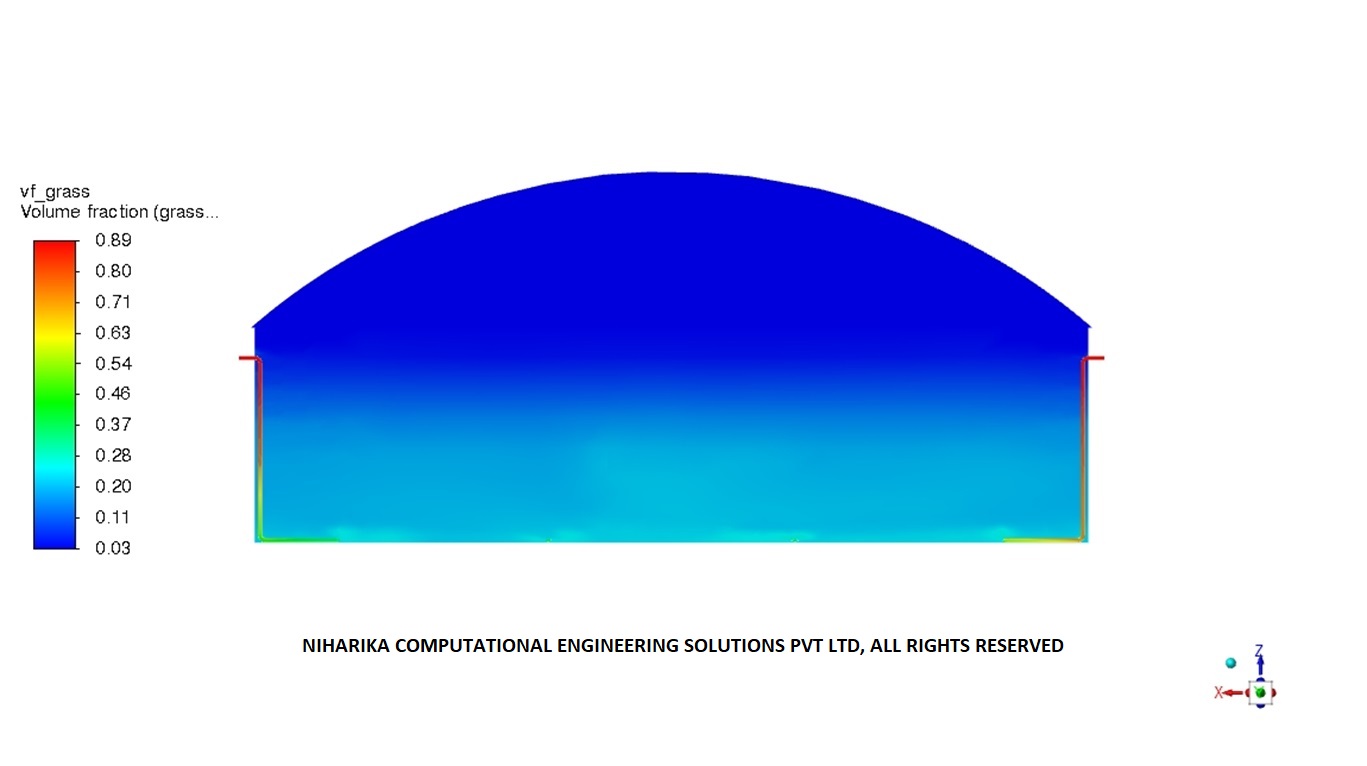
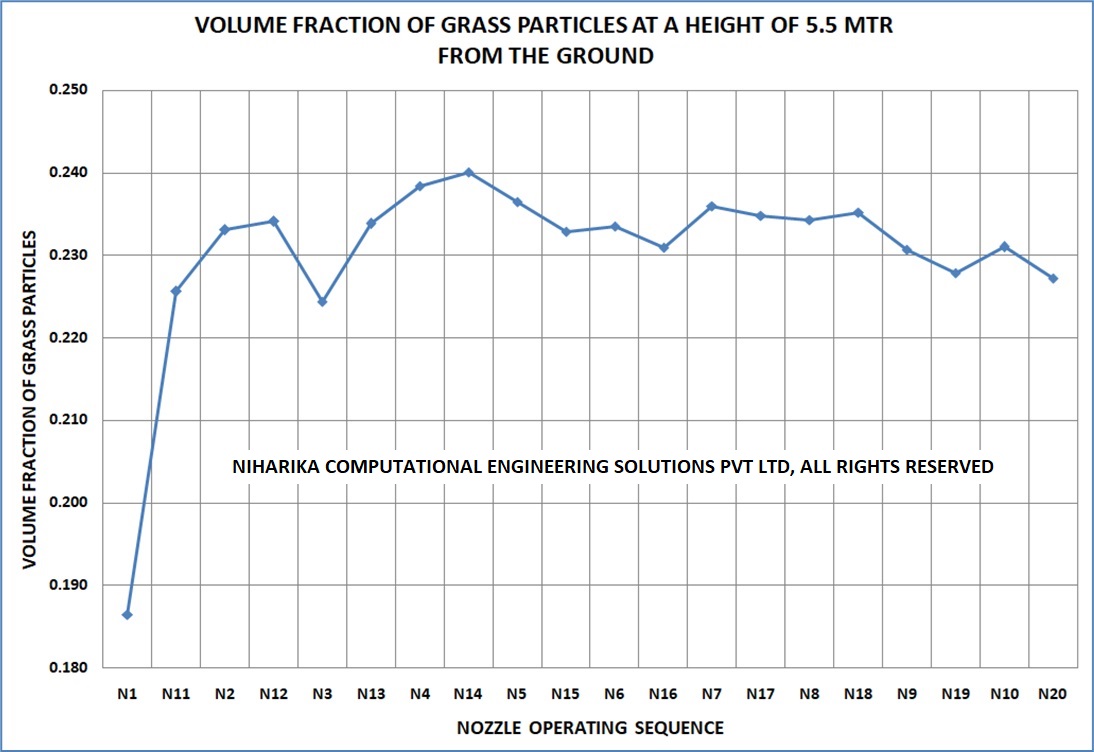
CFD analysis results
The enclosed graph indicates that throughout the nozzle operating sequence cycle, the volume fraction of Napier grass particles at a height of 5.5 meters from the ground has remained stable. This consistent pattern is also observed at various horizontal planes up to the maximum sludge height. Therefore, the agitation generated by the nozzle's operating sequence and the duration of gas firing is adequate in terms of operational and energy efficiency.
We Got More
Go through All Our Case Studies
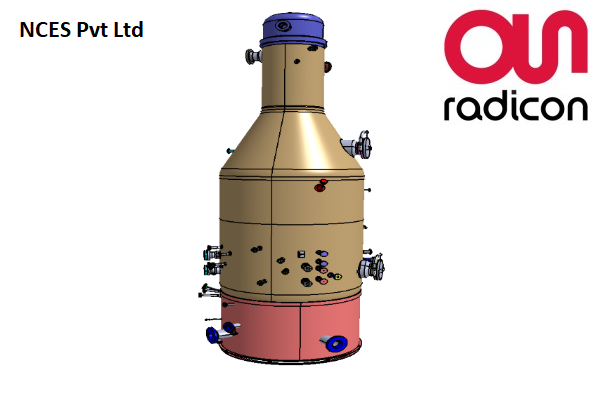
Mechanical and Structural design of Disk baffle for Oligomerisation reactor
We executed this project for a SABIC Petrochemical plant located in Al Jubail, Saudi Arabia. The proposed disk baffle is expected to serve the function of separating the condensate in the Oligomerisation reactor. We developed the conceptual model of the disk baffle using our expertise in core mechanical design and optimized the design using Finite Element Analysis (FEA). We provided detailed fabrication drawings to the customer and supported them during Fabrication process. Read More
CFD analysis of Helical Agitator
Helical agitators are a type of mixing equipment consisting of ribs or blades arranged in the form of a helix. This design creates axial motion and vigorous fluid motion inside a vessel. It is often used to mix viscous materials. The helical agitator is commonly used for low Reynolds number industrial mixing. The helical design of these agitators generates high shear rates and ensures thorough mixing of materials with different densities and viscosities. Helical agitators are used in polymer industries and other industries that require the use of quite viscous materials. Read More
CFD Analysis of Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer
Regenerative thermal oxidizers, commonly referred to as RTOs, are essential in the effective and economical removal of hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from industrial emissions. These thermal oxidizers are specialized combustion systems incorporated into the ventilation of industrial operations that produce potentially harmful pollutants. Read More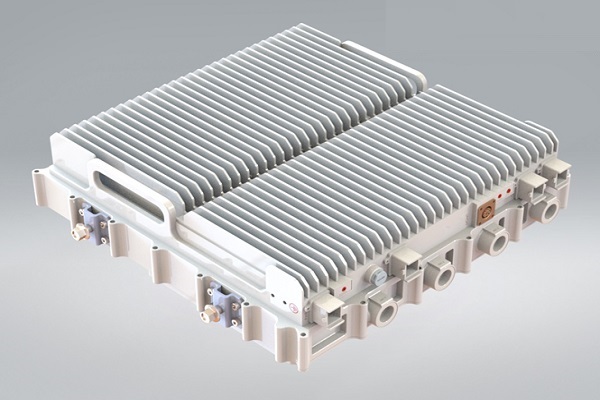
CFD analysis of Multi Band Remote Radio Unit
The advent of 5G technology has brought about unprecedented advancements in wireless communications, enabling faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. These advancements are associated with higher power consumption and increased heat generation in the 5G Remote Radio units.Increasing data rates and network densification require radio units to process larger volumes of data, leading to higher power consumption and heat generation. Environmental factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and exposure to direct sunlight also impact the thermal aspects of the radio units. Read More